SE4Binome2024-5
Aller à la navigation
Aller à la recherche
git : https://gitea.plil.fr/ktouron/se4-djadja-touron_pico.git
Carte fille clavier "matrice de touches"
Hardware
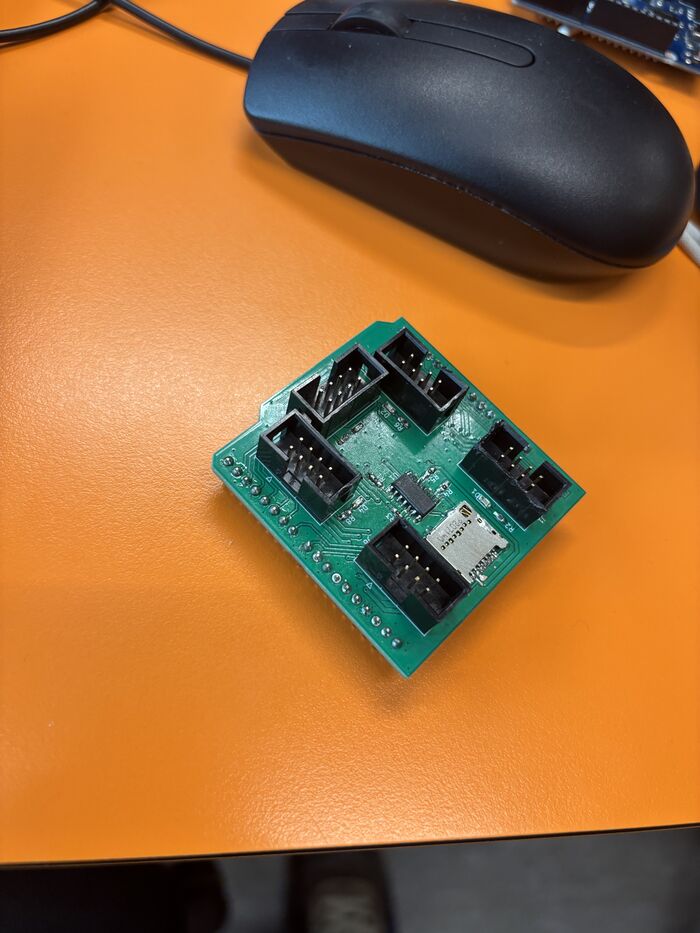
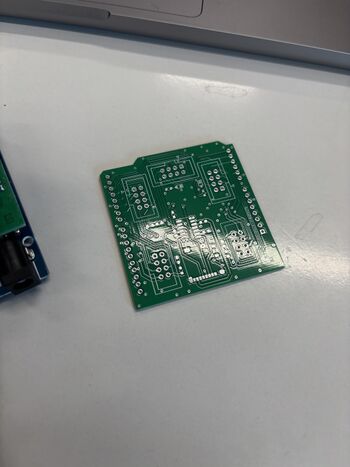
Carte Shield
Carte Shield après soudure des composants
Carte Fille
Carte Fille après soudure des composants
Software
Carte Shield
Allumage de LEDS sur Programmateur AVR
Avant de programmer directement sur le shield, nous avons allumé des LED pour tester la carte.
// the setup function runs once when you press reset or power the board
void setup() {
// initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output.
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop function runs over and over again forever
void loop() {
digitalWrite(1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(4, HIGH);
digitalWrite(7, HIGH);
digitalWrite(A0, HIGH);
digitalWrite(A3, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(1, LOW);
digitalWrite(4, LOW);
digitalWrite(7, LOW);
digitalWrite(A0, LOW);
digitalWrite(A3, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}
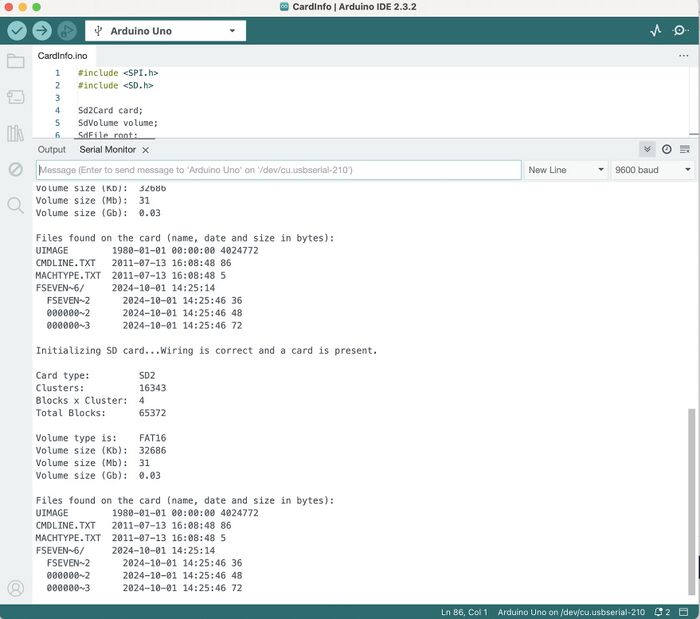
Test de lecture de la carte SD
Avant de programmer directement sur le shield, nous avons tester si la carte SD était bien détecté et lu
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
Sd2Card card;
SdVolume volume;
SdFile root;
const int chipSelect = 10;
void setup() {
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
}
Serial.print("\nInitializing SD card...");
// we'll use the initialization code from the utility libraries
// since we're just testing if the card is working!
if (!card.init(SPI_HALF_SPEED, chipSelect)) {
Serial.println("initialization failed. Things to check:");
Serial.println("* is a card inserted?");
Serial.println("* is your wiring correct?");
Serial.println("* did you change the chipSelect pin to match your shield or module?");
while (1);
} else {
Serial.println("Wiring is correct and a card is present.");
}
// print the type of card
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Card type: ");
switch (card.type()) {
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD1:
Serial.println("SD1");
break;
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2:
Serial.println("SD2");
break;
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC:
Serial.println("SDHC");
break;
default:
Serial.println("Unknown");
}
// Now we will try to open the 'volume'/'partition' - it should be FAT16 or FAT32
if (!volume.init(card)) {
Serial.println("Could not find FAT16/FAT32 partition.\nMake sure you've formatted the card");
while (1);
}
Serial.print("Clusters: ");
Serial.println(volume.clusterCount());
Serial.print("Blocks x Cluster: ");
Serial.println(volume.blocksPerCluster());
Serial.print("Total Blocks: ");
Serial.println(volume.blocksPerCluster() * volume.clusterCount());
Serial.println();
// print the type and size of the first FAT-type volume
uint32_t volumesize;
Serial.print("Volume type is: FAT");
Serial.println(volume.fatType(), DEC);
volumesize = volume.blocksPerCluster(); // clusters are collections of blocks
volumesize *= volume.clusterCount(); // we'll have a lot of clusters
volumesize /= 2; // SD card blocks are always 512 bytes (2 blocks are 1KB)
Serial.print("Volume size (Kb): ");
Serial.println(volumesize);
Serial.print("Volume size (Mb): ");
volumesize /= 1024;
Serial.println(volumesize);
Serial.print("Volume size (Gb): ");
Serial.println((float)volumesize / 1024.0);
Serial.println("\nFiles found on the card (name, date and size in bytes): ");
root.openRoot(volume);
// list all files in the card with date and size
root.ls(LS_R | LS_DATE | LS_SIZE);
}
void loop(void) {
}
Ordonnaceur
Allumer la LED broche PB5 avec Timer1 ISR
#define CTC1 WGM12 // Meilleur nom pour le bit
#define PERIODE 20
void init_minuteur(int diviseur,long periode){
TCCR1A=0; // Le mode choisi n'utilise pas ce registre
TCCR1B=(1<<CTC1); // Réinitialisation du minuteur sur expiration
switch(diviseur){
case 8: TCCR1B |= (1<<CS11); break;
case 64: TCCR1B |= (1<<CS11 | 11<<CS10); break;
case 256: TCCR1B |= (1<<CS12); break;
case 1024: TCCR1B |= (1<<CS12 | 1<<CS10); break;
}
// Un cycle prend 1/F_CPU secondes.
// Un pas de compteur prend diviseur/F_CPU secondes.
// Pour une periode en millisecondes, il faut (periode/1000)/(diviseur/F_CPU) pas
// soit (periode*F_CPU)/(1000*diviseur)
OCR1A=F_CPU/1000*periode/diviseur; // Calcul du pas
TCNT1=0; // Compteur initialisé
TIMSK1=(1<<OCIE1A); // Comparaison du compteur avec OCR1A
}
ISR(TIMER1_COMPA_vect/*, ISR_NAKED*/) // Procédure d'interruption
{
PORTB ^= (1 << PB5);
}
int main(void){
DDRB |= (1 << PB5);
init_minuteur(256,PERIODE);
sei();
while(1);
}
Macros de sauvegarde et restauration des registres
#define portSAVE_REGISTERS() \
asm volatile ( \
"push r0 \n\t" \
"in r0, __SREG__ \n\t"\
"cli \n\t" \
"push r0 \n\t"\
"push r1 \n\t" \
"clr r1 \n\t" \
"push r2 \n\t"\
"push r3 \n\t"\
"push r4 \n\t"\
"push r5 \n\t"\
"push r6 \n\t"\
"push r7 \n\t"\
"push r8 \n\t"\
"push r9 \n\t"\
"push r10 \n\t"\
"push r11 \n\t"\
"push r12 \n\t"\
"push r13 \n\t"\
"push r14 \n\t"\
"push r15 \n\t"\
"push r16 \n\t"\
"push r17 \n\t" \
"push r18 \n\t"\
"push r19 \n\t"\
"push r20 \n\t" \
"push r21 \n\t"\
"push r22 \n\t"\
"push r23 \n\t"\
"push r24 \n\t"\
"push r25 \n\t"\
"push r26 \n\t"\
"push r27 \n\t"\
"push r28 \n\t"\
"push r29 \n\t"\
"push r30 \n\t"\
"push r31 \n\t"\
);
#define portRESTORE_REGISTERS() \
asm volatile (\
"pop r31 \n\t" \
"pop r30 \n\t"\
"pop r29 \n\t" \
"pop r28 \n\t" \
"pop r27 \n\t" \
"pop r26 \n\t" \
"pop r25 \n\t"\
"pop r24 \n\t" \
"pop r23 \n\t" \
"pop r22 \n\t" \
"pop r21 \n\t" \
"pop r20 \n\t" \
"pop r19 \n\t" \
"pop r18 \n\t" \
"pop r17 \n\t" \
"pop r16 \n\t" \
"pop r15 \n\t" \
"pop r14 \n\t" \
"pop r13 \n\t" \
"pop r12 \n\t" \
"pop r11 \n\t" \
"pop r10 \n\t"\
"pop r9 \n\t" \
"pop r8 \n\t" \
"pop r7 \n\t" \
"pop r6 \n\t" \
"pop r5 \n\t" \
"pop r4 \n\t" \
"pop r3 \n\t" \
"pop r2 \n\t" \
"pop r1 \n\t" \
"pop r0 \n\t" \
"out __SREG__, r0 \n\t"\
"pop r0 \n\t" \
);
Coder le tableau des structures des processus
typedef struct {
uint16_t adresseDepart; //adresse de la fonction de départ
uint16_t adressePile; //adresse de la pile d'exécution
bool etat; //état du processus (1 ou 0)
} Process;
Process table_process[MAXPROCESS];
Coder la fonction d'initialisation de la pile d'un processus
A REMPLIR
Taches ∞ pour faire clignoter deux leds à 2 fréquences premières entre elle
A REMPLIR
Lancement des deux tâches en parallèle grâce à l'ordonnanceur à tourniquet
A REMPLIR